Platform
Solutions
Resources
Pricing
Entrar no visi
Platform
Solutions
Resources
Pricing
Entrar no visi
11 de ago. de 2025
11 de ago. de 2025
11 de ago. de 2025
What is BIM? Types, applications, and best practices
What is BIM? Types, applications, and best practices
Understand what BIM (Building Information Modeling) is. Check out its types, main applications, and best practices for using the methodology!
Understand what BIM (Building Information Modeling) is. Check out its types, main applications, and best practices for using the methodology!


Tales Silva
CEO & founder, Construct IN


Tales Silva
CEO & founder, Construct IN


Tales Silva
CEO & founder, Construct IN
cOMPARTILHE NAS REDES
cOMPARTILHE NAS REDES




*Cover image: Envato/YuriArcursPeopleimages
The construction industry has witnessed a significant transformation with the adoption of BIM Methodology (Building Information Modeling).
For civil engineers, this integration represents a fundamental shift in the way infrastructures are designed, built, and maintained.
In this article, learn more about BIM and how Visi, the management platform of Construct IN, integrated with this methodology, helps in monitoring construction sites.
Continue reading and check the details:
What is BIM?
The pillar of BIM: parametric 3D modeling
BIM 4D, 5D, 6D, and 7D
Types of data incorporated into BIM
Benefits of BIM in civil construction
BIM software available on the market
Best practices for using BIM
BIM BR Strategy: how it is transforming civil construction in Brazil?
FAQ: main questions about BIM
Integrate your BIM model with Visi
What is BIM?
BIM, an acronym for Building Information Modeling, is a methodology that allows the creation of three-dimensional models that aggregate detailed information about all the elements of a construction project. Let’s understand more?
The pillar of BIM: parametric 3D modeling
At the core of BIM is parametric 3D modeling, which allows the creation of detailed digital models that integrate geometric information and non-geometric data.
Unlike traditional CAD methods, where drawings are mostly two-dimensional, BIM provides an interactive three-dimensional visualization.
This parametric modeling is essential for coordination and clash detection, allowing changes to one component of the model to be automatically reflected across all associated documents.
BIM 4D, 5D, 6D and 7D
In addition to 3D modeling, there are other dimensions of BIM, such as time (4D), cost (5D), sustainability (6D), and facility management (7D).
See details about each one of them
4D: incorporates construction schedules into the 3D model, allowing for detailed simulation and planning of project phases;
5D: integrates cost estimates, providing a clear and accurate view of financial impacts throughout the project;
6D: refers to energy efficiency, environmental impact, among others;
7D: integrates facility management: maintenance, continuous use, operation, etc.
Types of data incorporated into BIM
1. Physical and material properties
Material composition: information about the types of materials, such as concrete, steel, and wood, including detailed specifications such as strength class (fck, fyk), density (ρ), and thermal conductivity (λ);
Dimensions and geometry: precise measurements of the elements, including length (L), width (B), height (H), and thickness (t). Also brings geometric variations and necessary tolerances for construction;
Weight and volume: data on the weight (W) and volume (V) of components, essential for structural and logistical calculations, such as load lifting and transportation.
2. Performance information
Load capacity: details about the load capacity of structural elements, including stress limits (σmax) and deformation (εmax), safety factors, and fatigue criteria;
Acoustic and thermal insulation: specifications about insulation performance, such as sound reduction index (Rw) and thermal resistance (R), helping to design comfortable and energy-efficient environments;
Durability and lifespan: information about the expected lifespan (LCA - Life Cycle Assessment) of materials and components, including maintenance data (MTBF - Mean Time Between Failures) and replacement cycles.
3. Construction and installation data
Construction methods: detailed instructions on construction and installation methods, including task sequencing (WBS - Work Breakdown Structure) and equipment requirements (lifting plans, scaffolding);
Schedules and sequences: integration with construction schedules (4D BIM), showing project phases and the order of element installation;
Cost and budget: detailed cost estimates (BoQ - Bill of Quantities), budgets (CAPEX/OPEX), and financial forecasts (cash flow analysis).
4. Sustainability information
Sustainability is a growing concern in civil engineering, and BIM 6D provides a robust platform for environmental performance analysis.
Through the integration of tools like Green Building Studio and Insight 360, engineers can conduct energy simulations and environmental impact assessments directly within the BIM model.
Environmental impact: data on carbon footprint (CO2 footprint) and energy efficiency (EUI - Energy Use Intensity);
Certifications and compliance: ISO 14001 (Environmental Management System) and NBR 15575 (Performance of Residential Buildings);
Performance simulations and other integrated environmental performance analyses with the BIM methodology.
- Read also: Sustainability in civil construction: importance and how to implement
5. Maintenance and operation data
Maintenance plans: detailed instructions for preventive maintenance (PM - Preventive Maintenance) and corrective maintenance (CM - Corrective Maintenance) of components, including schedules (maintenance schedules) and procedures (SOP - Standard Operating Procedures);
Maintenance history: record of maintenance activities performed, repairs, replacements, and inspections, stored in a CMMS (Computerized Maintenance Management System);
Technical documentation: manuals, technical specifications, warranties (warranty documents), and other relevant documents attached to the model components.
6. Usage and occupancy information
Function and use of spaces: details about the function of different areas and spaces within the construction, helping in planning occupancy and operation (space programming);
Accessibility and safety: data on accessibility (compliance with NBR 9050 - Accessibility for Buildings, Furniture, Spaces, and Equipment), emergency exits, fire protection systems, and safety standards (NR - Regulatory Norms of the Ministry of Labor and Employment).

Benefits of BIM in civil construction
BAIM's capability to integrate disciplines, such as architecture, structural engineering, electrical, and plumbing into a single collaborative model is one of its greatest advantages. This multidisciplinary integration facilitates coordination, significantly reducing design errors and rework.
- Read also: 7 steps to implement technology in civil construction
BIM software available on the market
There is a variety of BIM software available. The main ones are: Autodesk Revit, ArchiCAD, Bentley Systems AECOsim Building Designer, Trimble Connect, Nemetschek Allplan, among others.
Each one is designed to meet different needs, from architectural modeling and structural engineering to construction planning and model verification.
Best practices for using BIM
The first tip is to define clear and specific objectives for BIM implementation. Also, create a detailed execution plan that outlines the standards and procedures to be followed during the project. Other tips include:
1. Promote collaboration
Encourage collaboration among different disciplines (architecture, structure, and MEP) through workshops and integration sessions. BIM is more effective when used as a collaborative platform.
2. Quality and accuracy of models
Set and adopt consistent modeling standards to ensure uniformity and accuracy of models. Use standardized object libraries and ensure that all model elements are properly parameterized.
3. Continuous review and coordination
Conduct regular reviews of the model to detect and resolve conflicts (clash detection) before construction. Use tools to coordinate and integrate models from different disciplines.
4. Data and information management
Keep an organized and accessible data structure. Use data management platforms to store and share information efficiently. Document all changes and decisions in the BIM model.
5. Integration with planning and costs
Integrate the BIM model with construction schedules (4D BIM) to visualize project progress and plan activities efficiently. Use BIM for cost estimates (5D BIM) by integrating this information directly into the model.
6. Use BIM together with monitoring tools such as Visi
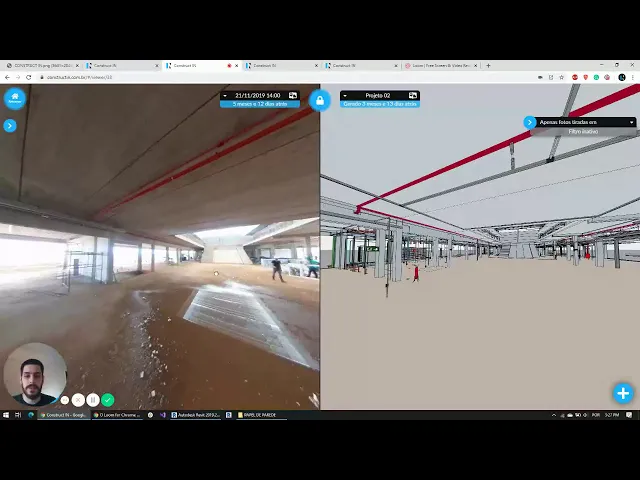
Integrating BIM with the Visi construction management system from Construct IN, is a good way to make a visual comparison between what was designed for the project and how it is being built. This is only possible because our tool allows you to take 360° images of the entire construction site in just a few minutes.
You don’t have to worry about noting the date the image was taken or about angles, as it is possible to define capture points directly on the submitted plan. In a few clicks, you will be able to compare on the screen: on one side what was designed in BIM and on the other the photo of the construction site.
See the details in this video:

To give you an overview of what else our tool can provide for you, read the post "Construct IN platform allows comparison between BIM project and construction execution in 360°".
Another reading that will also help you understand more about everything our platform can provide is "Construction management: how to do it and tips for good management".
7. Certification management
Use BIM to manage and monitor compliance with environmental certifications. Attach all necessary documentation to the model and track certification progress.
After project completion, the BIM model can be used for facilities management. Tools like ArchiFM or IBM Maximo can integrate BIM with facility management (FM) systems, optimizing operations and maintenance.
- Read also: BIM projects: application examples in Civil Construction
BIM BR Strategy: how is it transforming civil construction in Brazil?
The BIM BR Strategy is a federal government initiative to encourage the use of BIM in public works in Brazil. Created to modernize and make civil construction more efficient, it promotes the integration of different disciplines into a single model, increasing accuracy, reducing rework, and optimizing resources.
Led by the Managing Committee (CG-BIM) — with participation from ministries such as Industry, Science and Technology, Cities, and Planning — the strategy has nine main objectives, which include: popularizing BIM, training professionals, creating regulations, developing standards and technical guides, fostering investments, encouraging new technologies, and promoting open standards for interoperability.
With the adoption of BIM, the government expects to increase productivity, improve the quality of public works, reduce costs and deadlines, promote sustainability, and bring more transparency to bidding and execution.
FAQ: main questions about BIM
We have listed the main questions about the BIM methodology below. Some have already been answered throughout the text, but we've gathered everything in this section for your convenience.
What does BIM mean?
BIM stands for Building Information Modeling, or Modelagem da Informação da Construção in Portuguese.
What is BIM?
BIM is an innovative way of designing, building, and maintaining buildings and infrastructures. It allows for the creation of parametric 3D digital models that integrate geometric and non-geometric information, facilitating coordination among disciplines, avoiding conflicts, and optimizing resources.
What are the three main pillars of BIM?
The three most recognized pillars of BIM are: collaboration (integration among all disciplines and teams), coordination (organization and compatibility of information), and data integration (combining technical aspects, schedules, and costs in a single model).
What is the difference between CAD and BIM?
Traditional CAD mainly works with isolated 2D or 3D drawings, without a direct link to detailed construction information. BIM, on the other hand, integrates these drawings with complete project data, allowing for simulation, analysis, budgeting, and management throughout the entire project lifecycle.
What are BIM software?
There are various BIM software available on the market, including Autodesk Revit, ArchiCAD, Bentley Systems AECOsim Building Designer, Trimble Connect, and Nemetschek Allplan. Each one caters to different needs, ranging from architecture to planning and verification of works.
What is the most used BIM software in Brazil?
Autodesk Revit is one of the most popular BIM software in Brazil, widely used by architects, engineers, and construction companies for modeling, compatibility, and documentation of projects.
How much does the BIM program cost?
The cost varies according to the chosen software, contracted functionalities, and the number of licenses. In the case of Autodesk Revit, for example, the annual price is around several thousand reais, but there are options for monthly subscriptions and packages that include other Autodesk programs.
Integrate your BIM model with Visi
The Visi does not replace the need for on-site visits, but it reduces the cost and time spent on visits to the works. One example was construction company LK2, which reduced the time spent on this process from 1h30 to 20 minutes using our platform.
With our construction management software, you can track construction progress remotely through 360° images, integrate the BIM model, centralize all information in one place, generate dashboards and detailed reports (Non-Conformance, Construction Diary, Photographic Report of Works, etc).
Increase your productivity. Contact us and request a free demonstration.
The construction industry has witnessed a significant transformation with the adoption of BIM Methodology (Building Information Modeling).
For civil engineers, this integration represents a fundamental shift in the way infrastructures are designed, built, and maintained.
In this article, learn more about BIM and how Visi, the management platform of Construct IN, integrated with this methodology, helps in monitoring construction sites.
Continue reading and check the details:
What is BIM?
The pillar of BIM: parametric 3D modeling
BIM 4D, 5D, 6D, and 7D
Types of data incorporated into BIM
Benefits of BIM in civil construction
BIM software available on the market
Best practices for using BIM
BIM BR Strategy: how it is transforming civil construction in Brazil?
FAQ: main questions about BIM
Integrate your BIM model with Visi
What is BIM?
BIM, an acronym for Building Information Modeling, is a methodology that allows the creation of three-dimensional models that aggregate detailed information about all the elements of a construction project. Let’s understand more?
The pillar of BIM: parametric 3D modeling
At the core of BIM is parametric 3D modeling, which allows the creation of detailed digital models that integrate geometric information and non-geometric data.
Unlike traditional CAD methods, where drawings are mostly two-dimensional, BIM provides an interactive three-dimensional visualization.
This parametric modeling is essential for coordination and clash detection, allowing changes to one component of the model to be automatically reflected across all associated documents.
BIM 4D, 5D, 6D and 7D
In addition to 3D modeling, there are other dimensions of BIM, such as time (4D), cost (5D), sustainability (6D), and facility management (7D).
See details about each one of them
4D: incorporates construction schedules into the 3D model, allowing for detailed simulation and planning of project phases;
5D: integrates cost estimates, providing a clear and accurate view of financial impacts throughout the project;
6D: refers to energy efficiency, environmental impact, among others;
7D: integrates facility management: maintenance, continuous use, operation, etc.
Types of data incorporated into BIM
1. Physical and material properties
Material composition: information about the types of materials, such as concrete, steel, and wood, including detailed specifications such as strength class (fck, fyk), density (ρ), and thermal conductivity (λ);
Dimensions and geometry: precise measurements of the elements, including length (L), width (B), height (H), and thickness (t). Also brings geometric variations and necessary tolerances for construction;
Weight and volume: data on the weight (W) and volume (V) of components, essential for structural and logistical calculations, such as load lifting and transportation.
2. Performance information
Load capacity: details about the load capacity of structural elements, including stress limits (σmax) and deformation (εmax), safety factors, and fatigue criteria;
Acoustic and thermal insulation: specifications about insulation performance, such as sound reduction index (Rw) and thermal resistance (R), helping to design comfortable and energy-efficient environments;
Durability and lifespan: information about the expected lifespan (LCA - Life Cycle Assessment) of materials and components, including maintenance data (MTBF - Mean Time Between Failures) and replacement cycles.
3. Construction and installation data
Construction methods: detailed instructions on construction and installation methods, including task sequencing (WBS - Work Breakdown Structure) and equipment requirements (lifting plans, scaffolding);
Schedules and sequences: integration with construction schedules (4D BIM), showing project phases and the order of element installation;
Cost and budget: detailed cost estimates (BoQ - Bill of Quantities), budgets (CAPEX/OPEX), and financial forecasts (cash flow analysis).
4. Sustainability information
Sustainability is a growing concern in civil engineering, and BIM 6D provides a robust platform for environmental performance analysis.
Through the integration of tools like Green Building Studio and Insight 360, engineers can conduct energy simulations and environmental impact assessments directly within the BIM model.
Environmental impact: data on carbon footprint (CO2 footprint) and energy efficiency (EUI - Energy Use Intensity);
Certifications and compliance: ISO 14001 (Environmental Management System) and NBR 15575 (Performance of Residential Buildings);
Performance simulations and other integrated environmental performance analyses with the BIM methodology.
- Read also: Sustainability in civil construction: importance and how to implement
5. Maintenance and operation data
Maintenance plans: detailed instructions for preventive maintenance (PM - Preventive Maintenance) and corrective maintenance (CM - Corrective Maintenance) of components, including schedules (maintenance schedules) and procedures (SOP - Standard Operating Procedures);
Maintenance history: record of maintenance activities performed, repairs, replacements, and inspections, stored in a CMMS (Computerized Maintenance Management System);
Technical documentation: manuals, technical specifications, warranties (warranty documents), and other relevant documents attached to the model components.
6. Usage and occupancy information
Function and use of spaces: details about the function of different areas and spaces within the construction, helping in planning occupancy and operation (space programming);
Accessibility and safety: data on accessibility (compliance with NBR 9050 - Accessibility for Buildings, Furniture, Spaces, and Equipment), emergency exits, fire protection systems, and safety standards (NR - Regulatory Norms of the Ministry of Labor and Employment).

Benefits of BIM in civil construction
BAIM's capability to integrate disciplines, such as architecture, structural engineering, electrical, and plumbing into a single collaborative model is one of its greatest advantages. This multidisciplinary integration facilitates coordination, significantly reducing design errors and rework.
- Read also: 7 steps to implement technology in civil construction
BIM software available on the market
There is a variety of BIM software available. The main ones are: Autodesk Revit, ArchiCAD, Bentley Systems AECOsim Building Designer, Trimble Connect, Nemetschek Allplan, among others.
Each one is designed to meet different needs, from architectural modeling and structural engineering to construction planning and model verification.
Best practices for using BIM
The first tip is to define clear and specific objectives for BIM implementation. Also, create a detailed execution plan that outlines the standards and procedures to be followed during the project. Other tips include:
1. Promote collaboration
Encourage collaboration among different disciplines (architecture, structure, and MEP) through workshops and integration sessions. BIM is more effective when used as a collaborative platform.
2. Quality and accuracy of models
Set and adopt consistent modeling standards to ensure uniformity and accuracy of models. Use standardized object libraries and ensure that all model elements are properly parameterized.
3. Continuous review and coordination
Conduct regular reviews of the model to detect and resolve conflicts (clash detection) before construction. Use tools to coordinate and integrate models from different disciplines.
4. Data and information management
Keep an organized and accessible data structure. Use data management platforms to store and share information efficiently. Document all changes and decisions in the BIM model.
5. Integration with planning and costs
Integrate the BIM model with construction schedules (4D BIM) to visualize project progress and plan activities efficiently. Use BIM for cost estimates (5D BIM) by integrating this information directly into the model.
6. Use BIM together with monitoring tools such as Visi
Integrating BIM with the Visi construction management system from Construct IN, is a good way to make a visual comparison between what was designed for the project and how it is being built. This is only possible because our tool allows you to take 360° images of the entire construction site in just a few minutes.
You don’t have to worry about noting the date the image was taken or about angles, as it is possible to define capture points directly on the submitted plan. In a few clicks, you will be able to compare on the screen: on one side what was designed in BIM and on the other the photo of the construction site.
See the details in this video:

To give you an overview of what else our tool can provide for you, read the post "Construct IN platform allows comparison between BIM project and construction execution in 360°".
Another reading that will also help you understand more about everything our platform can provide is "Construction management: how to do it and tips for good management".
7. Certification management
Use BIM to manage and monitor compliance with environmental certifications. Attach all necessary documentation to the model and track certification progress.
After project completion, the BIM model can be used for facilities management. Tools like ArchiFM or IBM Maximo can integrate BIM with facility management (FM) systems, optimizing operations and maintenance.
- Read also: BIM projects: application examples in Civil Construction
BIM BR Strategy: how is it transforming civil construction in Brazil?
The BIM BR Strategy is a federal government initiative to encourage the use of BIM in public works in Brazil. Created to modernize and make civil construction more efficient, it promotes the integration of different disciplines into a single model, increasing accuracy, reducing rework, and optimizing resources.
Led by the Managing Committee (CG-BIM) — with participation from ministries such as Industry, Science and Technology, Cities, and Planning — the strategy has nine main objectives, which include: popularizing BIM, training professionals, creating regulations, developing standards and technical guides, fostering investments, encouraging new technologies, and promoting open standards for interoperability.
With the adoption of BIM, the government expects to increase productivity, improve the quality of public works, reduce costs and deadlines, promote sustainability, and bring more transparency to bidding and execution.
FAQ: main questions about BIM
We have listed the main questions about the BIM methodology below. Some have already been answered throughout the text, but we've gathered everything in this section for your convenience.
What does BIM mean?
BIM stands for Building Information Modeling, or Modelagem da Informação da Construção in Portuguese.
What is BIM?
BIM is an innovative way of designing, building, and maintaining buildings and infrastructures. It allows for the creation of parametric 3D digital models that integrate geometric and non-geometric information, facilitating coordination among disciplines, avoiding conflicts, and optimizing resources.
What are the three main pillars of BIM?
The three most recognized pillars of BIM are: collaboration (integration among all disciplines and teams), coordination (organization and compatibility of information), and data integration (combining technical aspects, schedules, and costs in a single model).
What is the difference between CAD and BIM?
Traditional CAD mainly works with isolated 2D or 3D drawings, without a direct link to detailed construction information. BIM, on the other hand, integrates these drawings with complete project data, allowing for simulation, analysis, budgeting, and management throughout the entire project lifecycle.
What are BIM software?
There are various BIM software available on the market, including Autodesk Revit, ArchiCAD, Bentley Systems AECOsim Building Designer, Trimble Connect, and Nemetschek Allplan. Each one caters to different needs, ranging from architecture to planning and verification of works.
What is the most used BIM software in Brazil?
Autodesk Revit is one of the most popular BIM software in Brazil, widely used by architects, engineers, and construction companies for modeling, compatibility, and documentation of projects.
How much does the BIM program cost?
The cost varies according to the chosen software, contracted functionalities, and the number of licenses. In the case of Autodesk Revit, for example, the annual price is around several thousand reais, but there are options for monthly subscriptions and packages that include other Autodesk programs.
Integrate your BIM model with Visi
The Visi does not replace the need for on-site visits, but it reduces the cost and time spent on visits to the works. One example was construction company LK2, which reduced the time spent on this process from 1h30 to 20 minutes using our platform.
With our construction management software, you can track construction progress remotely through 360° images, integrate the BIM model, centralize all information in one place, generate dashboards and detailed reports (Non-Conformance, Construction Diary, Photographic Report of Works, etc).
Increase your productivity. Contact us and request a free demonstration.
The construction industry has witnessed a significant transformation with the adoption of BIM Methodology (Building Information Modeling).
For civil engineers, this integration represents a fundamental shift in the way infrastructures are designed, built, and maintained.
In this article, learn more about BIM and how Visi, the management platform of Construct IN, integrated with this methodology, helps in monitoring construction sites.
Continue reading and check the details:
What is BIM?
The pillar of BIM: parametric 3D modeling
BIM 4D, 5D, 6D, and 7D
Types of data incorporated into BIM
Benefits of BIM in civil construction
BIM software available on the market
Best practices for using BIM
BIM BR Strategy: how it is transforming civil construction in Brazil?
FAQ: main questions about BIM
Integrate your BIM model with Visi
What is BIM?
BIM, an acronym for Building Information Modeling, is a methodology that allows the creation of three-dimensional models that aggregate detailed information about all the elements of a construction project. Let’s understand more?
The pillar of BIM: parametric 3D modeling
At the core of BIM is parametric 3D modeling, which allows the creation of detailed digital models that integrate geometric information and non-geometric data.
Unlike traditional CAD methods, where drawings are mostly two-dimensional, BIM provides an interactive three-dimensional visualization.
This parametric modeling is essential for coordination and clash detection, allowing changes to one component of the model to be automatically reflected across all associated documents.
BIM 4D, 5D, 6D and 7D
In addition to 3D modeling, there are other dimensions of BIM, such as time (4D), cost (5D), sustainability (6D), and facility management (7D).
See details about each one of them
4D: incorporates construction schedules into the 3D model, allowing for detailed simulation and planning of project phases;
5D: integrates cost estimates, providing a clear and accurate view of financial impacts throughout the project;
6D: refers to energy efficiency, environmental impact, among others;
7D: integrates facility management: maintenance, continuous use, operation, etc.
Types of data incorporated into BIM
1. Physical and material properties
Material composition: information about the types of materials, such as concrete, steel, and wood, including detailed specifications such as strength class (fck, fyk), density (ρ), and thermal conductivity (λ);
Dimensions and geometry: precise measurements of the elements, including length (L), width (B), height (H), and thickness (t). Also brings geometric variations and necessary tolerances for construction;
Weight and volume: data on the weight (W) and volume (V) of components, essential for structural and logistical calculations, such as load lifting and transportation.
2. Performance information
Load capacity: details about the load capacity of structural elements, including stress limits (σmax) and deformation (εmax), safety factors, and fatigue criteria;
Acoustic and thermal insulation: specifications about insulation performance, such as sound reduction index (Rw) and thermal resistance (R), helping to design comfortable and energy-efficient environments;
Durability and lifespan: information about the expected lifespan (LCA - Life Cycle Assessment) of materials and components, including maintenance data (MTBF - Mean Time Between Failures) and replacement cycles.
3. Construction and installation data
Construction methods: detailed instructions on construction and installation methods, including task sequencing (WBS - Work Breakdown Structure) and equipment requirements (lifting plans, scaffolding);
Schedules and sequences: integration with construction schedules (4D BIM), showing project phases and the order of element installation;
Cost and budget: detailed cost estimates (BoQ - Bill of Quantities), budgets (CAPEX/OPEX), and financial forecasts (cash flow analysis).
4. Sustainability information
Sustainability is a growing concern in civil engineering, and BIM 6D provides a robust platform for environmental performance analysis.
Through the integration of tools like Green Building Studio and Insight 360, engineers can conduct energy simulations and environmental impact assessments directly within the BIM model.
Environmental impact: data on carbon footprint (CO2 footprint) and energy efficiency (EUI - Energy Use Intensity);
Certifications and compliance: ISO 14001 (Environmental Management System) and NBR 15575 (Performance of Residential Buildings);
Performance simulations and other integrated environmental performance analyses with the BIM methodology.
- Read also: Sustainability in civil construction: importance and how to implement
5. Maintenance and operation data
Maintenance plans: detailed instructions for preventive maintenance (PM - Preventive Maintenance) and corrective maintenance (CM - Corrective Maintenance) of components, including schedules (maintenance schedules) and procedures (SOP - Standard Operating Procedures);
Maintenance history: record of maintenance activities performed, repairs, replacements, and inspections, stored in a CMMS (Computerized Maintenance Management System);
Technical documentation: manuals, technical specifications, warranties (warranty documents), and other relevant documents attached to the model components.
6. Usage and occupancy information
Function and use of spaces: details about the function of different areas and spaces within the construction, helping in planning occupancy and operation (space programming);
Accessibility and safety: data on accessibility (compliance with NBR 9050 - Accessibility for Buildings, Furniture, Spaces, and Equipment), emergency exits, fire protection systems, and safety standards (NR - Regulatory Norms of the Ministry of Labor and Employment).

Benefits of BIM in civil construction
BAIM's capability to integrate disciplines, such as architecture, structural engineering, electrical, and plumbing into a single collaborative model is one of its greatest advantages. This multidisciplinary integration facilitates coordination, significantly reducing design errors and rework.
- Read also: 7 steps to implement technology in civil construction
BIM software available on the market
There is a variety of BIM software available. The main ones are: Autodesk Revit, ArchiCAD, Bentley Systems AECOsim Building Designer, Trimble Connect, Nemetschek Allplan, among others.
Each one is designed to meet different needs, from architectural modeling and structural engineering to construction planning and model verification.
Best practices for using BIM
The first tip is to define clear and specific objectives for BIM implementation. Also, create a detailed execution plan that outlines the standards and procedures to be followed during the project. Other tips include:
1. Promote collaboration
Encourage collaboration among different disciplines (architecture, structure, and MEP) through workshops and integration sessions. BIM is more effective when used as a collaborative platform.
2. Quality and accuracy of models
Set and adopt consistent modeling standards to ensure uniformity and accuracy of models. Use standardized object libraries and ensure that all model elements are properly parameterized.
3. Continuous review and coordination
Conduct regular reviews of the model to detect and resolve conflicts (clash detection) before construction. Use tools to coordinate and integrate models from different disciplines.
4. Data and information management
Keep an organized and accessible data structure. Use data management platforms to store and share information efficiently. Document all changes and decisions in the BIM model.
5. Integration with planning and costs
Integrate the BIM model with construction schedules (4D BIM) to visualize project progress and plan activities efficiently. Use BIM for cost estimates (5D BIM) by integrating this information directly into the model.
6. Use BIM together with monitoring tools such as Visi
Integrating BIM with the Visi construction management system from Construct IN, is a good way to make a visual comparison between what was designed for the project and how it is being built. This is only possible because our tool allows you to take 360° images of the entire construction site in just a few minutes.
You don’t have to worry about noting the date the image was taken or about angles, as it is possible to define capture points directly on the submitted plan. In a few clicks, you will be able to compare on the screen: on one side what was designed in BIM and on the other the photo of the construction site.
See the details in this video:

To give you an overview of what else our tool can provide for you, read the post "Construct IN platform allows comparison between BIM project and construction execution in 360°".
Another reading that will also help you understand more about everything our platform can provide is "Construction management: how to do it and tips for good management".
7. Certification management
Use BIM to manage and monitor compliance with environmental certifications. Attach all necessary documentation to the model and track certification progress.
After project completion, the BIM model can be used for facilities management. Tools like ArchiFM or IBM Maximo can integrate BIM with facility management (FM) systems, optimizing operations and maintenance.
- Read also: BIM projects: application examples in Civil Construction
BIM BR Strategy: how is it transforming civil construction in Brazil?
The BIM BR Strategy is a federal government initiative to encourage the use of BIM in public works in Brazil. Created to modernize and make civil construction more efficient, it promotes the integration of different disciplines into a single model, increasing accuracy, reducing rework, and optimizing resources.
Led by the Managing Committee (CG-BIM) — with participation from ministries such as Industry, Science and Technology, Cities, and Planning — the strategy has nine main objectives, which include: popularizing BIM, training professionals, creating regulations, developing standards and technical guides, fostering investments, encouraging new technologies, and promoting open standards for interoperability.
With the adoption of BIM, the government expects to increase productivity, improve the quality of public works, reduce costs and deadlines, promote sustainability, and bring more transparency to bidding and execution.
FAQ: main questions about BIM
We have listed the main questions about the BIM methodology below. Some have already been answered throughout the text, but we've gathered everything in this section for your convenience.
What does BIM mean?
BIM stands for Building Information Modeling, or Modelagem da Informação da Construção in Portuguese.
What is BIM?
BIM is an innovative way of designing, building, and maintaining buildings and infrastructures. It allows for the creation of parametric 3D digital models that integrate geometric and non-geometric information, facilitating coordination among disciplines, avoiding conflicts, and optimizing resources.
What are the three main pillars of BIM?
The three most recognized pillars of BIM are: collaboration (integration among all disciplines and teams), coordination (organization and compatibility of information), and data integration (combining technical aspects, schedules, and costs in a single model).
What is the difference between CAD and BIM?
Traditional CAD mainly works with isolated 2D or 3D drawings, without a direct link to detailed construction information. BIM, on the other hand, integrates these drawings with complete project data, allowing for simulation, analysis, budgeting, and management throughout the entire project lifecycle.
What are BIM software?
There are various BIM software available on the market, including Autodesk Revit, ArchiCAD, Bentley Systems AECOsim Building Designer, Trimble Connect, and Nemetschek Allplan. Each one caters to different needs, ranging from architecture to planning and verification of works.
What is the most used BIM software in Brazil?
Autodesk Revit is one of the most popular BIM software in Brazil, widely used by architects, engineers, and construction companies for modeling, compatibility, and documentation of projects.
How much does the BIM program cost?
The cost varies according to the chosen software, contracted functionalities, and the number of licenses. In the case of Autodesk Revit, for example, the annual price is around several thousand reais, but there are options for monthly subscriptions and packages that include other Autodesk programs.
Integrate your BIM model with Visi
The Visi does not replace the need for on-site visits, but it reduces the cost and time spent on visits to the works. One example was construction company LK2, which reduced the time spent on this process from 1h30 to 20 minutes using our platform.
With our construction management software, you can track construction progress remotely through 360° images, integrate the BIM model, centralize all information in one place, generate dashboards and detailed reports (Non-Conformance, Construction Diary, Photographic Report of Works, etc).
Increase your productivity. Contact us and request a free demonstration.
The construction industry has witnessed a significant transformation with the adoption of BIM Methodology (Building Information Modeling).
For civil engineers, this integration represents a fundamental shift in the way infrastructures are designed, built, and maintained.
In this article, learn more about BIM and how Visi, the management platform of Construct IN, integrated with this methodology, helps in monitoring construction sites.
Continue reading and check the details:
What is BIM?
The pillar of BIM: parametric 3D modeling
BIM 4D, 5D, 6D, and 7D
Types of data incorporated into BIM
Benefits of BIM in civil construction
BIM software available on the market
Best practices for using BIM
BIM BR Strategy: how it is transforming civil construction in Brazil?
FAQ: main questions about BIM
Integrate your BIM model with Visi
What is BIM?
BIM, an acronym for Building Information Modeling, is a methodology that allows the creation of three-dimensional models that aggregate detailed information about all the elements of a construction project. Let’s understand more?
The pillar of BIM: parametric 3D modeling
At the core of BIM is parametric 3D modeling, which allows the creation of detailed digital models that integrate geometric information and non-geometric data.
Unlike traditional CAD methods, where drawings are mostly two-dimensional, BIM provides an interactive three-dimensional visualization.
This parametric modeling is essential for coordination and clash detection, allowing changes to one component of the model to be automatically reflected across all associated documents.
BIM 4D, 5D, 6D and 7D
In addition to 3D modeling, there are other dimensions of BIM, such as time (4D), cost (5D), sustainability (6D), and facility management (7D).
See details about each one of them
4D: incorporates construction schedules into the 3D model, allowing for detailed simulation and planning of project phases;
5D: integrates cost estimates, providing a clear and accurate view of financial impacts throughout the project;
6D: refers to energy efficiency, environmental impact, among others;
7D: integrates facility management: maintenance, continuous use, operation, etc.
Types of data incorporated into BIM
1. Physical and material properties
Material composition: information about the types of materials, such as concrete, steel, and wood, including detailed specifications such as strength class (fck, fyk), density (ρ), and thermal conductivity (λ);
Dimensions and geometry: precise measurements of the elements, including length (L), width (B), height (H), and thickness (t). Also brings geometric variations and necessary tolerances for construction;
Weight and volume: data on the weight (W) and volume (V) of components, essential for structural and logistical calculations, such as load lifting and transportation.
2. Performance information
Load capacity: details about the load capacity of structural elements, including stress limits (σmax) and deformation (εmax), safety factors, and fatigue criteria;
Acoustic and thermal insulation: specifications about insulation performance, such as sound reduction index (Rw) and thermal resistance (R), helping to design comfortable and energy-efficient environments;
Durability and lifespan: information about the expected lifespan (LCA - Life Cycle Assessment) of materials and components, including maintenance data (MTBF - Mean Time Between Failures) and replacement cycles.
3. Construction and installation data
Construction methods: detailed instructions on construction and installation methods, including task sequencing (WBS - Work Breakdown Structure) and equipment requirements (lifting plans, scaffolding);
Schedules and sequences: integration with construction schedules (4D BIM), showing project phases and the order of element installation;
Cost and budget: detailed cost estimates (BoQ - Bill of Quantities), budgets (CAPEX/OPEX), and financial forecasts (cash flow analysis).
4. Sustainability information
Sustainability is a growing concern in civil engineering, and BIM 6D provides a robust platform for environmental performance analysis.
Through the integration of tools like Green Building Studio and Insight 360, engineers can conduct energy simulations and environmental impact assessments directly within the BIM model.
Environmental impact: data on carbon footprint (CO2 footprint) and energy efficiency (EUI - Energy Use Intensity);
Certifications and compliance: ISO 14001 (Environmental Management System) and NBR 15575 (Performance of Residential Buildings);
Performance simulations and other integrated environmental performance analyses with the BIM methodology.
- Read also: Sustainability in civil construction: importance and how to implement
5. Maintenance and operation data
Maintenance plans: detailed instructions for preventive maintenance (PM - Preventive Maintenance) and corrective maintenance (CM - Corrective Maintenance) of components, including schedules (maintenance schedules) and procedures (SOP - Standard Operating Procedures);
Maintenance history: record of maintenance activities performed, repairs, replacements, and inspections, stored in a CMMS (Computerized Maintenance Management System);
Technical documentation: manuals, technical specifications, warranties (warranty documents), and other relevant documents attached to the model components.
6. Usage and occupancy information
Function and use of spaces: details about the function of different areas and spaces within the construction, helping in planning occupancy and operation (space programming);
Accessibility and safety: data on accessibility (compliance with NBR 9050 - Accessibility for Buildings, Furniture, Spaces, and Equipment), emergency exits, fire protection systems, and safety standards (NR - Regulatory Norms of the Ministry of Labor and Employment).

Benefits of BIM in civil construction
BAIM's capability to integrate disciplines, such as architecture, structural engineering, electrical, and plumbing into a single collaborative model is one of its greatest advantages. This multidisciplinary integration facilitates coordination, significantly reducing design errors and rework.
- Read also: 7 steps to implement technology in civil construction
BIM software available on the market
There is a variety of BIM software available. The main ones are: Autodesk Revit, ArchiCAD, Bentley Systems AECOsim Building Designer, Trimble Connect, Nemetschek Allplan, among others.
Each one is designed to meet different needs, from architectural modeling and structural engineering to construction planning and model verification.
Best practices for using BIM
The first tip is to define clear and specific objectives for BIM implementation. Also, create a detailed execution plan that outlines the standards and procedures to be followed during the project. Other tips include:
1. Promote collaboration
Encourage collaboration among different disciplines (architecture, structure, and MEP) through workshops and integration sessions. BIM is more effective when used as a collaborative platform.
2. Quality and accuracy of models
Set and adopt consistent modeling standards to ensure uniformity and accuracy of models. Use standardized object libraries and ensure that all model elements are properly parameterized.
3. Continuous review and coordination
Conduct regular reviews of the model to detect and resolve conflicts (clash detection) before construction. Use tools to coordinate and integrate models from different disciplines.
4. Data and information management
Keep an organized and accessible data structure. Use data management platforms to store and share information efficiently. Document all changes and decisions in the BIM model.
5. Integration with planning and costs
Integrate the BIM model with construction schedules (4D BIM) to visualize project progress and plan activities efficiently. Use BIM for cost estimates (5D BIM) by integrating this information directly into the model.
6. Use BIM together with monitoring tools such as Visi
Integrating BIM with the Visi construction management system from Construct IN, is a good way to make a visual comparison between what was designed for the project and how it is being built. This is only possible because our tool allows you to take 360° images of the entire construction site in just a few minutes.
You don’t have to worry about noting the date the image was taken or about angles, as it is possible to define capture points directly on the submitted plan. In a few clicks, you will be able to compare on the screen: on one side what was designed in BIM and on the other the photo of the construction site.
See the details in this video:

To give you an overview of what else our tool can provide for you, read the post "Construct IN platform allows comparison between BIM project and construction execution in 360°".
Another reading that will also help you understand more about everything our platform can provide is "Construction management: how to do it and tips for good management".
7. Certification management
Use BIM to manage and monitor compliance with environmental certifications. Attach all necessary documentation to the model and track certification progress.
After project completion, the BIM model can be used for facilities management. Tools like ArchiFM or IBM Maximo can integrate BIM with facility management (FM) systems, optimizing operations and maintenance.
- Read also: BIM projects: application examples in Civil Construction
BIM BR Strategy: how is it transforming civil construction in Brazil?
The BIM BR Strategy is a federal government initiative to encourage the use of BIM in public works in Brazil. Created to modernize and make civil construction more efficient, it promotes the integration of different disciplines into a single model, increasing accuracy, reducing rework, and optimizing resources.
Led by the Managing Committee (CG-BIM) — with participation from ministries such as Industry, Science and Technology, Cities, and Planning — the strategy has nine main objectives, which include: popularizing BIM, training professionals, creating regulations, developing standards and technical guides, fostering investments, encouraging new technologies, and promoting open standards for interoperability.
With the adoption of BIM, the government expects to increase productivity, improve the quality of public works, reduce costs and deadlines, promote sustainability, and bring more transparency to bidding and execution.
FAQ: main questions about BIM
We have listed the main questions about the BIM methodology below. Some have already been answered throughout the text, but we've gathered everything in this section for your convenience.
What does BIM mean?
BIM stands for Building Information Modeling, or Modelagem da Informação da Construção in Portuguese.
What is BIM?
BIM is an innovative way of designing, building, and maintaining buildings and infrastructures. It allows for the creation of parametric 3D digital models that integrate geometric and non-geometric information, facilitating coordination among disciplines, avoiding conflicts, and optimizing resources.
What are the three main pillars of BIM?
The three most recognized pillars of BIM are: collaboration (integration among all disciplines and teams), coordination (organization and compatibility of information), and data integration (combining technical aspects, schedules, and costs in a single model).
What is the difference between CAD and BIM?
Traditional CAD mainly works with isolated 2D or 3D drawings, without a direct link to detailed construction information. BIM, on the other hand, integrates these drawings with complete project data, allowing for simulation, analysis, budgeting, and management throughout the entire project lifecycle.
What are BIM software?
There are various BIM software available on the market, including Autodesk Revit, ArchiCAD, Bentley Systems AECOsim Building Designer, Trimble Connect, and Nemetschek Allplan. Each one caters to different needs, ranging from architecture to planning and verification of works.
What is the most used BIM software in Brazil?
Autodesk Revit is one of the most popular BIM software in Brazil, widely used by architects, engineers, and construction companies for modeling, compatibility, and documentation of projects.
How much does the BIM program cost?
The cost varies according to the chosen software, contracted functionalities, and the number of licenses. In the case of Autodesk Revit, for example, the annual price is around several thousand reais, but there are options for monthly subscriptions and packages that include other Autodesk programs.
Integrate your BIM model with Visi
The Visi does not replace the need for on-site visits, but it reduces the cost and time spent on visits to the works. One example was construction company LK2, which reduced the time spent on this process from 1h30 to 20 minutes using our platform.
With our construction management software, you can track construction progress remotely through 360° images, integrate the BIM model, centralize all information in one place, generate dashboards and detailed reports (Non-Conformance, Construction Diary, Photographic Report of Works, etc).
Increase your productivity. Contact us and request a free demonstration.
*Cover image: Envato/YuriArcursPeopleimages
*Cover image: Envato/YuriArcursPeopleimages
*Cover image: Envato/YuriArcursPeopleimages
*Cover image: Envato/YuriArcursPeopleimages
Sobre o autor


Tales Silva
CEO & founder, Construct IN


Tales Silva
CEO & founder, Construct IN


Tales Silva
CEO & founder, Construct IN
Tales Silva é Engenheiro Civil formado pela PUCRS (2016) e possui MBA Executivo com foco em marketing pela ESPM-Sul (2019). Tem experiência em projetos estruturais e em construções industrializadas. É fundador e CEO da Construct IN, construtech que oferece uma plataforma de gestão e documentação de obras por meio de imagens 360º.
cOMPARTILHE NAS REDES
Recomendado para você
carregar mais ↓
Subscribe to our newsletter
Subscribe to our newsletter
Subscribe to our newsletter
Explora nossas ferramentas
Entra em contato e descobre como dados e tecnologia podem ser a solução que tu precisas.
Conhece as ferramentas →

Avenida Unisinos, 950 UNITEC 1 - G12 / Sala 120
- Cristo Rei, 93022-750
R. Cerro Corá, 2175, Spaces, Sala 605 - Construct IN, Vila Romana, 05061-450
R. Leocádia Pedra dos Santos, 115, Base 27, Sala Construct IN - Enseada do Suá, 29050-370
English (United States)
Avenida Unisinos, 950 UNITEC 1 - G12 / Sala 120
- Cristo Rei, 93022-750
R. Cerro Corá, 2175, Spaces, Sala 605 - Construct IN, Vila Romana, 05061-450
R. Leocádia Pedra dos Santos, 115, Base 27, Sala Construct IN - Enseada do Suá, 29050-370
English (United States)
Avenida Unisinos, 950 UNITEC 1 - G12 / Sala 120
- Cristo Rei, 93022-750
R. Cerro Corá, 2175, Spaces, Sala 605 - Construct IN, Vila Romana, 05061-450
R. Leocádia Pedra dos Santos, 115, Base 27, Sala Construct IN - Enseada do Suá, 29050-370
English (United States)
Avenida Unisinos, 950 UNITEC 1 - G12 / Sala 120
- Cristo Rei, 93022-750
R. Cerro Corá, 2175, Spaces, Sala 605 - Construct IN, Vila Romana, 05061-450
R. Leocádia Pedra dos Santos, 115, Base 27, Sala Construct IN - Enseada do Suá, 29050-370
English (United States)